Vantage 3.0
Introducing a hybrid approach to using Document AI and GenAI
Supercharge AI automation with the power of reliable, accurate OCR
Increase straight-through document processing with data-driven insights
Integrate reliable Document AI in your automation workflows with just a few lines of code
PROCESS UNDERSTANDING
PROCESS OPTIMIZATION
Purpose-built AI for limitless automation.
Kick-start your automation with pre-trained AI extraction models.
Meet our contributors, explore assets, and more.
BY INDUSTRY
BY BUSINESS PROCESS
BY TECHNOLOGY
Build
Integrate advanced text recognition capabilities into your applications and workflows via API.
AI-ready document data for context grounded GenAI output with RAG.
Explore purpose-built AI for Intelligent Automation.
Grow
Connect with peers and experienced OCR, IDP, and AI professionals.
A distinguished title awarded to developers who demonstrate exceptional expertise in ABBYY AI.
Explore
Insights
Implementation
August 13, 2025
Just a few years ago, intelligent automation that combined artificial intelligence (AI) with automation tools was considered the big shift—yet today, the focus has already jumped to agentic automation that gives AI the ability to make decisions and act on its own. In this blog, we’ll look at how these two approaches compare, where they overlap, and what agentic automation could mean for the future of work.
Jump to:
What is intelligent automation?
Benefits of intelligent automation
Examples and use cases for intelligent automation
Benefits of agentic automation
Examples and use cases for agentic automation
Key differences between intelligent automation and agentic automation
Intelligent automation is the combination of AI technologies and robotic process automation (RPA) that allows you to streamline even complex workflows with minimal manual effort.
Previously, automation was fairly limited, following simple, rule-based instructions to complete repetitive tasks like copying and pasting data between systems. But as AI matured, automation started getting paired with cognitive capabilities—like the ability to understand documents and extract context-specific information. Today, intelligent automation can take care of most of the manual work in process tasks such as claims or customer requests. As a result, businesses can complete workflows much faster and at a lower cost with fewer errors.

A key way intelligent automation supports healthcare teams is by relieving the burden of administrative tasks such as claims processing and referral management. Offloading these repetitive processes to technology that handles them accurately accelerates and improves service and care—and gives providers more time to care for patients.
Financial services teams manage a high volume of documents alongside strict compliance requirements. Intelligent automation—especially through intelligent document processing (IDP)—helps by processing documents at scale. This allows for faster loan approvals, improved Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance, greater insight into chargebacks, and other enhancements.
Intelligent automation helps insurance teams work more optimally across the entire policy lifecycle by streamlining claims intake, improving access to customer data, and much more. Ultimately, both employees and customers can enjoy a more seamless experience.
By digitizing and automating documentation across the shipping lifecycle, intelligent automation eliminates manual entry, helps speed up customs clearance, and tracks warehouse data for transportation and logistics teams.
In shared services centers, intelligent automation can improve data accuracy and efficiency across core tasks like invoice processing, expense categorization, real-time reporting, and record reconciliation.
Customer onboarding becomes easier with intelligent automation. This smart technology can remove manual steps by allowing users to upload documents with a photo, automate identity verification through facial matching, and eliminate data entry.
Agentic automation is the use of intelligent agents—AI-driven systems that can make decisions and take action on their own—to automate complex tasks. By combining technologies like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and decision-making frameworks, these agents can respond to inputs, learn from outcomes, and improve over time. Unlike traditional automation, which follows fixed rules, agentic automation adapts to changing conditions and handles dynamic, unpredictable processes with minimal human intervention.
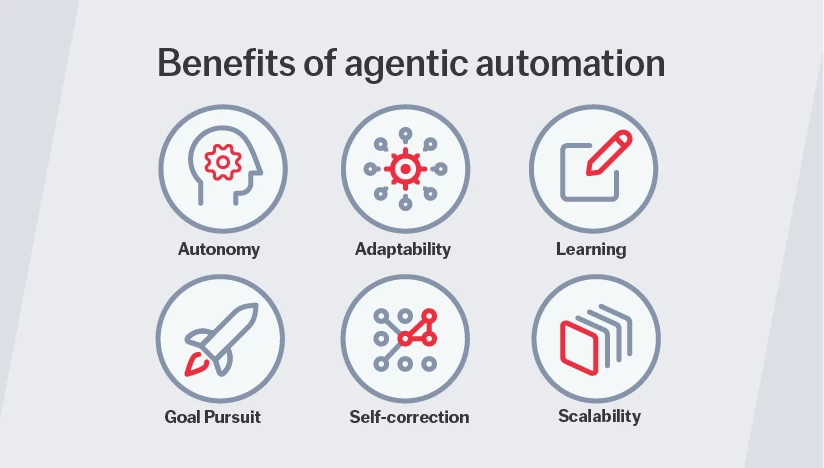
Make smarter decisions automatically: Agentic automation enables AI systems to make decisions autonomously and take action without human input. This way, technology systems can manage entire workflows end-to-end rather than just assisting or following pre-set rules.
Adapt instantly to change: Agentic automation can adjust in real time based on new data or changing conditions without needing to be reprogrammed. Businesses can react with greater speed and agility to emerging challenges or opportunities.
Continuously improve: Through feedback and experience, agentic automation can refine its actions over time to complete tasks more efficiently and make better decisions quickly.
Achieve goals: Instead of simply completing individual tasks, agentic automation can pursue the goals behind those tasks to better adapt dynamically.
Resolve issues without escalation: Instead of escalating anomalies immediately to human workers, agentic automation can learn to resolve unexpected situations on its own, choosing alternative actions or learning from past decisions.
Scale automation enterprise-wide: Because agents can operate independently across systems and processes, agentic automation allows organizations to scale complex, adaptive workflows without constant human oversight.
Agentic automation helps insurance teams move faster by autonomously analyzing submitted claims, extracting relevant data, and validating coverage. For straightforward cases, AI agents can even complete the entire process, from intake to approval, without human involvement.
In healthcare, agentic automation can go beyond administrative support to assist in care optimization and clinical decision-making. It can evaluate patient symptoms, review medical histories, and prioritize cases for triage.
Agentic automation brings intelligent, real-time decision-making to financial workflows. It can analyze transaction data for fraud detection, assess loan applications, monitor risk, and more while improving consistency and reducing human bias.
For government agencies, agentic automation enables enhanced service delivery. Smart technology can autonomously process and verify applications, flag discrepancies, make approval or denial decisions, and streamline workflows for services like benefits administration and tax processing.
Agentic automation enhances service by going beyond scripted responses to independently resolve common customer issues, such as issuing refunds or prioritizing inquiries. Customers get responsive, more personalized experiences without the need for human intervention.
| Intelligent automation (IA) | Agentic automation | |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Streamline and optimize workflows with AI-enhanced efficiency. | Enable autonomous decision-making and action with minimal human input. |
| Human involvement | Semi-autonomous, depending on human input for exceptions, logic setup, or escalations. | Fully autonomous in many scenarios and capable of reasoning and acting without constant human oversight. |
| Decision-making | Relies on rules, models, or historical data for semi-automated decision-making. | Makes independent decisions that adapt based on goals, changing inputs, and conditions. |
| Error handling | Identifies anomalies and flags them or follows predefined correction paths. | Attempts at self-correction even for unusual situations, only escalating when needed. |
| Use cases | Best for defined, relatively predictable processes like invoice processing or compliance checks. | Best for more complex, dynamic processes like customer dispute resolution or adaptive pricing. |
Since intelligent and agentic automation offer different strengths, consider the following criteria to pick the best approach for your business.
Type of process: Use intelligent automation for structured, rule-based processes like document processing and agentic automation when processes are dynamic or require flexible, multi-step decision-making such as supply chain adjustments.
Level of autonomy needed: Go with agentic automation when you need AI agents to make decisions and take action independently with minimal or no human oversight. Opt for intelligent automation if you’d like typical scenarios to be handled automatically but can escalate any special cases or anomalies to human workers.
Complexity: Intelligent automation scales well for repeatable, high-volume tasks across departments. If you’d like to automate complex operations where decisions vary based on real-time data, patterns, or goals, agentic automation is likely the better fit.
Speed and adaptability: Intelligent automation delivers speed and consistency across known processes. Agentic automation adds adaptability that lets systems respond in real time to evolving conditions.
For businesses across industries, automating processes is foundational to staying competitive. This is especially true for document-intensive workflows, which are often manual, complex, and critical to areas like compliance, customer service, and operational efficiency. That’s why organizations around the world rely on ABBYY’s Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and Process Intelligence (PI) to fuel automation at scale.
ABBYY IDP transforms unstructured content into structured, trustworthy data, while ABBYY PI delivers real-time insight into how processes actually run. Together, they enable intelligent and agentic automation by eliminating blind spots and providing the context-rich information AI agents need to operate autonomously—making decisions, adapting to change, and driving continuous improvement with confidence and accountability.
With IDP and PI working in tandem, businesses can unlock a new level of precision, agility, and resilience. To explore how ABBYY’s solutions can support your automation goals, connect with one of our experts today.