Vantage 3.0
Introducing a hybrid approach to using Document AI and GenAI
Supercharge AI automation with the power of reliable, accurate OCR
Increase straight-through document processing with data-driven insights
Integrate reliable Document AI in your automation workflows with just a few lines of code
PROCESS UNDERSTANDING
PROCESS OPTIMIZATION
Purpose-built AI for limitless automation.
Kick-start your automation with pre-trained AI extraction models.
Meet our contributors, explore assets, and more.
BY INDUSTRY
BY BUSINESS PROCESS
BY TECHNOLOGY
Build
Integrate advanced text recognition capabilities into your applications and workflows via API.
AI-ready document data for context grounded GenAI output with RAG.
Explore purpose-built AI for Intelligent Automation.
Grow
Connect with peers and experienced OCR, IDP, and AI professionals.
A distinguished title awarded to developers who demonstrate exceptional expertise in ABBYY AI.
Explore
Insights
Implementation
September 26, 2025
Companies put a lot of effort into designing processes, but many still lack visibility into how those workflows actually run. Although business process management (BPM) tools can help design how work should be done, they aren’t built to map or monitor day-to-day execution.
After a workflow is implemented, reality tends to stray from the plan. In real life, employees may cut corners, or systems fail to talk to each other.
Seeing how processes really run on the ground requires a different solution: process mining. Process mining sifts through the data in your systems to show you how your processes truly run, including where things slow down and what could be improved.
Many teams confuse BPM and process mining, but the two serve very different, if complementary, roles. Understanding the difference between the two lets you make data-driven workflow improvements that BPM alone can’t deliver.
Jump to:
Business process management (BPM) explained
Process mining vs business process management (BPM)
What BPM can’t show you, but process mining can
Why BPM and process mining work better together
Common questions about BPM, process mining, and process intelligence
ABBYY Timeline: Your end-to-end process intelligence platform
Business process management (BPM) refers to the practice and the technologies for designing and orchestrating the way work gets done across an organization, with the goal to execute and optimize processes. When done well, BPM:
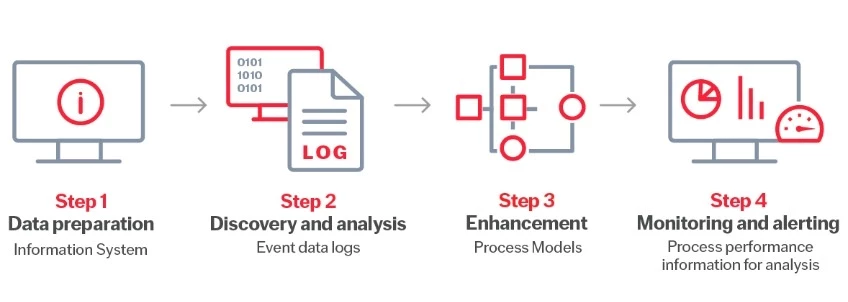
Process mining refers to the techniques and technologies used to transform event logs from IT systems into visual process maps. These data-driven maps show businesses the way their processes truly run. Process mining helps businesses:
Business process management (BPM) and process mining tackle process improvement from different angles. BPM designs how work should happen by creating structure and rules, while process mining looks at what’s really happening by analyzing data from your systems.
| BPM | Process Mining | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To design and optimize how business processes should work. | To uncover how processes actually run by analyzing real system data. |
| When to use | To define or redesign workflows. | To assess and optimize existing processes. |
| Tools | Workflow design and orchestration tools focused on ideal process execution. | Data-driven analysis tools that map real-world process behavior based on system activity logs. |
| Approach | Model-driven, based on ideal process flows. | Data-driven, based on reconstructing real workflows from system event logs. |
| Time to value | Moderate to long. Requires process modeling and implementation. | Fast. Driven by data ingestion and automated analysis. |
| Data source | Process documentation, business rules, user input, and modeled workflows. | Event logs from business systems like CRM, EHR, and ERP. |
Used together, BPM and process mining help teams shift from one-time process design to a continuous cycle of process optimization.
Business process management (BPM) is the go-to tool for designing structured, standardized workflows, but by itself, it has a blind spot: execution visibility. Once processes are up and running, you need process mining to see what’s really happening in your business.
With process mining, businesses gain:
Processes rarely unfold in real life the way they were originally designed. Yet to make smart real-life decisions, businesses need to know how work happens on the ground.
This is especially true during major organizational shifts that require clear process lead time metrics. As highlighted by EY, a leading consumer healthcare company that needed to separate its consumer goods business from its pharmaceutical division turned to process mining to map its workflows.
The goal was to identify hidden dependencies or potential disruptions to the transition. Teams then streamlined handoffs and minimized process disruptions while untangling operations across departments.
Without a clear view of how processes actually run, it’s nearly impossible to make informed decisions. Process mining fills that gap.
One Fortune 100 financial institution, for example, used process mining to consolidate data from over 40 systems into a live stream of two million daily event records. This gave the company a real-time view of transaction workflows and pinpointed $6 million in avoidable expenses tied to delays and manual handling.
Process mining pulls up-to-date information to let businesses see how processes are running at the moment, as well as historically. According to a report by CIO, when the state of Oklahoma set out to audit billions in public spending across 122 agencies, the Office of Management and Enterprise Services (OMES) used process mining to pull live data into a centralized dashboard. The team got visibility into purchase orders and card transactions for real-time oversight over 100% of state spending.
Process mining also allows businesses to move from isolated fixes to an ongoing cycle of optimization. The same CIO report, for example, details how Albini & Pitigliani, a global freight and logistics company, used a process mining platform to analyze logs and uncover inefficiencies.
By using real-time KPI dashboards, area managers could view the performance of different traffic types and tweak workflows as needed. Over time, ALPI reduced fulfillment errors by 75% while increasing sales by 15%.
All of these examples required information that BPM alone couldn’t provide: a clear understanding of how work was actually getting done, often uncovered through techniques like root cause analysis and process conformance. Process mining delivers that visibility across industries, whether the goal is saving taxpayer dollars or navigating a complex business separation.
Process improvement doesn’t stop at designing better workflows, but requires making sure those workflows actually work. As a result, many organizations pair BPM with process mining: BPM lays out the structure, and process mining puts it to the test.
Together, the two technologies help close the gap between planning and execution. Teams can spot smarter improvement and automation opportunities and continue tweaking processes to make them run even better.
Traditional BPM shows you how processes should work. Yet in the real world, delays and variations often make processes deviate from the ideal. Process mining analyzes real system data to show how work flows in practice.
BPM is used to design and maintain ideal workflows, while process mining uses system data to show how processes run in real life. Process intelligence combines process mining with a broader set of data-driven capabilities covering process discovery, analysis, monitoring, prediction, and simulation.
Businesses often turn to BPM to design structured workflows, then bring in process mining to visualize how those workflows actually run. Process intelligence brings these capabilities together, combining mining, monitoring, and prediction using AI tools to give teams the full picture needed to optimize processes.
Yes. BPM provides the blueprint for how work should get done, but process intelligence shows how it’s actually happening. Without both, you risk overlooking inefficiencies that drag down performance or missing opportunities to improve and innovate.
Process mining often uncovers a gap between workflows designed by BPM methods and what happens in practice. While BPM defines the ideal process, process mining shows the reality. Teams need this reality check to identify inefficiencies and hidden opportunities that traditional models can’t capture.
At ABBYY, we’ve spent decades helping enterprises make their processes smarter and faster. Our process intelligence platform ABBYY Timeline combines the power of process mining and task mining to give organizations a clear, data-driven view of how work actually happens.
Timeline goes beyond process mining to offer AI-driven capabilities for process discovery, analysis, monitoring, prediction, and simulation. Watch our 1-minute introduction video to see how this all-in-one approach works. Then start your free trial of ABBYY Timeline or get in touch with one of our experts to experience the value firsthand.