Vantage 3.0
Introducing a hybrid approach to using Document AI and GenAI
Supercharge AI automation with the power of reliable, accurate OCR
Increase straight-through document processing with data-driven insights
Integrate reliable Document AI in your automation workflows with just a few lines of code
PROCESS UNDERSTANDING
PROCESS OPTIMIZATION
Purpose-built AI for limitless automation.
Kick-start your automation with pre-trained AI extraction models.
Meet our contributors, explore assets, and more.
BY INDUSTRY
BY BUSINESS PROCESS
BY TECHNOLOGY
Build
Integrate advanced text recognition capabilities into your applications and workflows via API.
AI-ready document data for context grounded GenAI output with RAG.
Explore purpose-built AI for Intelligent Automation.
Grow
Connect with peers and experienced OCR, IDP, and AI professionals.
A distinguished title awarded to developers who demonstrate exceptional expertise in ABBYY AI.
Explore
Insights
Implementation
January 15, 2026
Generative AI can perform impressive tasks, but it has a well-known flaw: It sometimes “hallucinates” and makes up answers that sound right but aren’t.
To get the benefits of large language models (LLMs) without the misinformation, many businesses are pairing them with another AI technology: retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
RAG helps LLMs give more accurate, trustworthy answers by linking them to external data sources with relevant information. Agentic RAG takes this technology further to also plan, decide, and act on those answers. To put it simply, RAG retrieves facts, while agentic RAG uses those facts to make decisions and take actions.
Let’s take a look at how both traditional RAG and agentic RAG work, what their benefits and limitations are, and how to choose the right one for your business.
Jump to:
Understanding how traditional RAG works
Understanding how agentic RAG works
RAG vs Agentic RAG: Key differences at a glance
Why agentic RAG alone can’t work in isolation
How ABBYY builds a strong foundation for RAG and agentic RAG
RAG is an AI approach designed to make LLMs more accurate and reliable. Instead of relying only on the data they were trained on, RAG systems connect LLMs to trusted documents or databases to pull in up-to-date, relevant materials before generating a response. This way, LLMs can ground their answers in real evidence and give more reliable, context-aware answers.
The main benefits of RAG include:
RAG systems rely on a number of components that work together:
Traditional RAG, however, comes with some limitations:
Here’s how the traditional RAG workflow typically works:
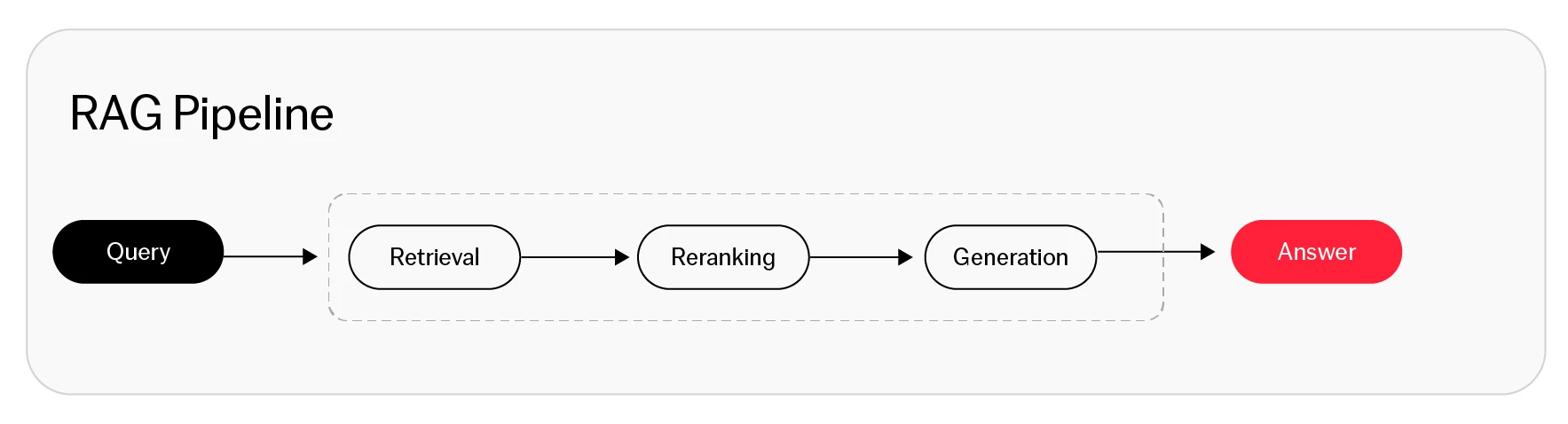
Agentic RAG strengthens LLMs by not only grounding their responses in external, verifiable sources but also adding the ability to reason, make decisions, and take action based on what they learn.
Basically, while traditional RAG simply gives responses, agentic RAG can also act on these responses like an active participant in problem-solving.
Agentic RAG adds reasoning, decision-making, and action to the traditional RAG workflow:
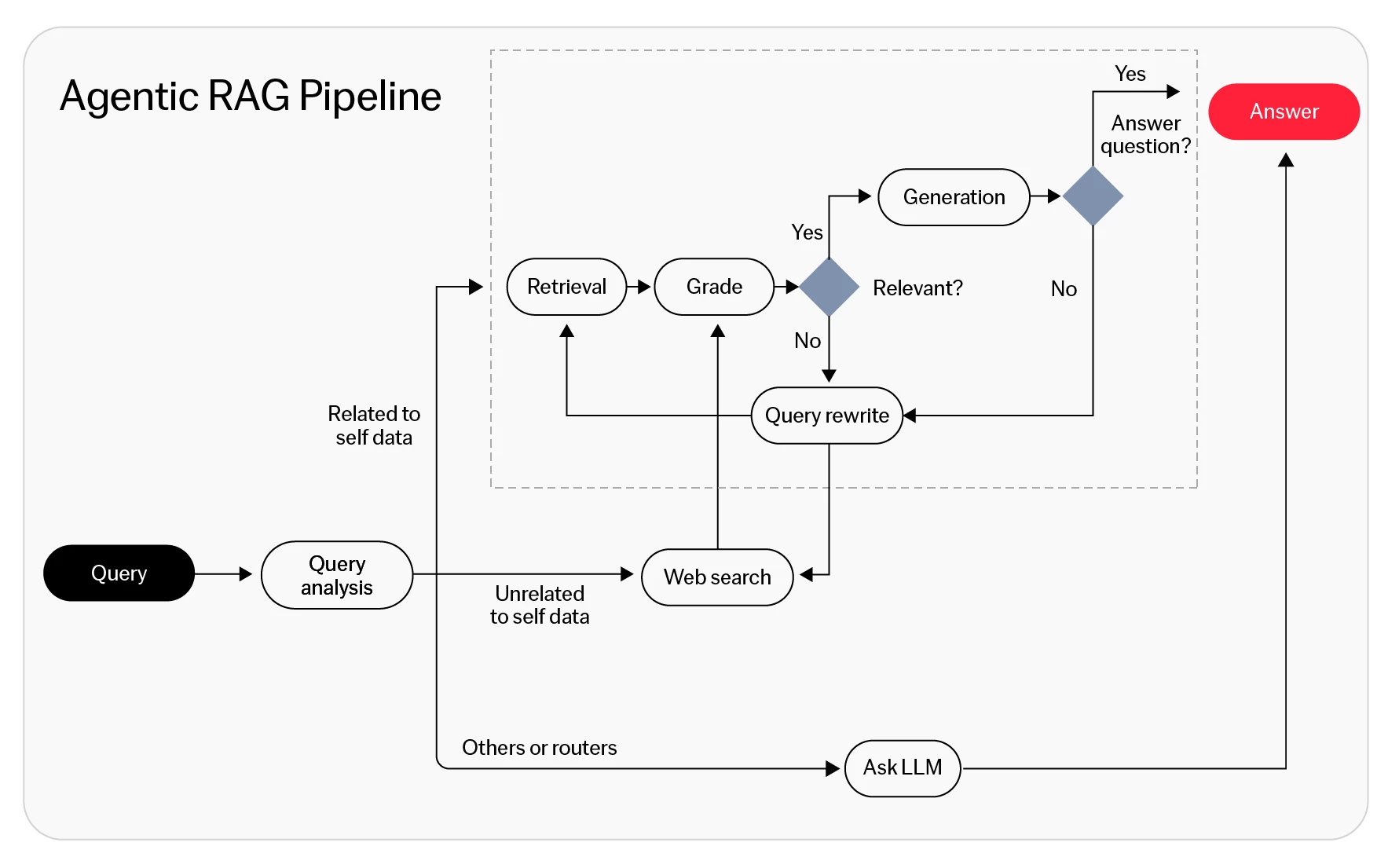
Traditional RAG improves LLM accuracy, while agentic RAG goes further to identify gaps, retrieve additional data when needed, validate information, and take action.
| RAG | Agentic RAG | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI architecture that improves LLM performance by connecting them to external knowledge sources | Advanced RAG architecture that incorporates intelligent agents to reason, plan, validate, and act |
| Use case | Knowledge retrieval, FAQs, summarizing information | Complex tasks like: decision support, automated workflows, multi-step problem solving |
| Adaptability | Relies on a pre-indexed knowledge base and reacts only to user prompts | Performs multiple searches to refine results as necessary |
| Accuracy | Grounds responses in external data to improve precision | Further improves precision by validating and cross-checking responses |
| Focus | Grounds responses in trustworthy information to reduce hallucinations | Uses grounded knowledge to reason, decide, and take action |
| Limitation | Dependent on the quality and scope of its data sources; limited to retrieval and summarization | Dependent on the quality and scope of its data sources |
| Efficiency and cost | Generally faster and less resource-intensive | More capable, but also more expensive and complex to design and operate |
In short, RAG helps LLMs provide context-grounded answers quickly, while agentic RAG adds reasoning and validation for more accurate, reliable outcomes.
As versatile and powerful as agentic RAG is, used on its own, the technology comes up against limits:
Strong data quality is the foundation of any successful RAG system, traditional or agentic. This is what ABBYY Document AI provides. By turning unstructured content into clean, structured, and semantically rich data, ABBYY gives RAG models a trusted base of truth to reason from. Agentic RAG delivers intelligence, but ABBYY delivers the reliable data that makes that intelligence work.
By automating document extraction and structuring, ABBYY also reduces the noise and redundancy that slow down retrieval and reasoning. Additionally, ABBYY simplifies the technical side of deploying agentic RAG by offering structured data pipelines and API-based integrations.
To see how ABBYY Document AI augments RAG, watch this three-minute demo video. To explore how ABBYY can strengthen your RAG or agentic RAG initiatives, connect with one of our experts.
Yes. Many organizations begin with RAG to ground language models in verified data. Once that’s established, you can extend into agentic RAG and scale toward more autonomous, goal-driven systems as data maturity grows.
RAG enhances LLMs by retrieving and grounding their responses in external knowledge sources. Agentic RAG, builds on this by enabling the system to reason, decide, and act based on the information it retrieves.
Highly regulated industries such as finance, insurance, and healthcare gain clear value, but any organization with documents can benefit, because when document data becomes structured and accessible, it becomes actionable.
Yes. ABBYY Document AI works seamlessly with RAG platforms and LLMs through APIs and ready-to-use connectors. It sends structured, validated data straight into vector databases and retrieval pipelines to improve how models reason and respond.